Rise in Heart Disease on a Global Scale

Hiral Patel
October 13, 2022

Hiral Patel
October 13, 2022
Heart disease, principally ischemic heart attack and stroke, remains the leading cause of disease burden globally. The decades-long rise of heart disease remains a cause of concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This surge in heart disease is due to multiple factors like diet, lifestyle changes, genetics, globalisation, and shift in the healthcare system. However, there is progress in the fight against heart diseases. And it is necessary to create awareness to combat this growing epidemic.
Think about the stark contrast in the diet of our great-grandparents because they ate local, fresh, and in-season foods. Today, a large portion of our diet consists of processed, packaged foods. Diet is only one component that contributes to heart disease globally. Other causative factors often fail to attract the awareness and emphasis it deserves.
Heart disease refers to those diseases that affect your heart. It is a medical condition that tends to damage the structure or impair the function of your heart. Most people think of heart disease as a single condition. But it is a group of disorders with many different root causes, collectively called cardiovascular diseases. According to curated statistical data, around 18.2 million adults aged 20 and older have coronary heart disease.
Data also shows coronary heart disease prevalence rates in India. Over the past several decades, it has been estimated to range from 1.6% to 7.4% in rural populations and from 1% to 13.2% in urban populations.
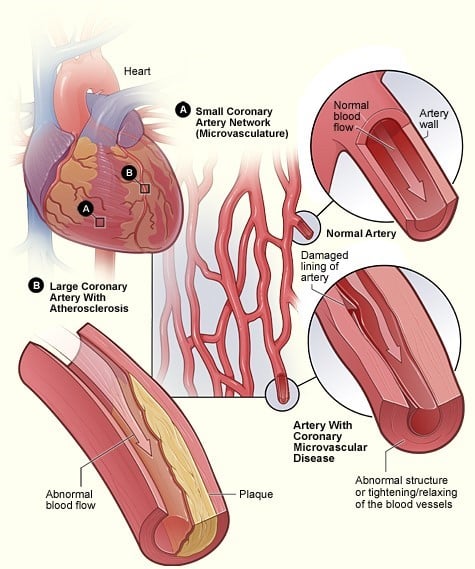
Coronary artery disease happens when the coronary arteries that carry blood to your heart get blocked. It is the most common form of heart disease.
The blockage or plaque collection in the blood vessels is called atherosclerosis. Over time, plaque can harden inside of your arterial walls. When it does, it blocks blood flow to your heart. Coronary artery disease can also lead to other heart problems, including heart failure and arrhythmias.

Heart rhythm disorders or arrhythmia impact the pumping action and make your heartbeat too slow or quick. It might also cause uncoordinated contractions. There are many heart rhythm disorders, and some have no warning signs.
Structural heart disease refers to heart structure abnormalities. It affects the walls, muscles, valves, or blood vessels of the heart. People living with this type of heart disease need support throughout every age and stage of their life. It often requires ongoing medical care and surgical procedures.
Heart failure is a heart disease that stands as the world’s leading cause of hospitalisation. It develops after the heart becomes weakened or damaged. Heart failure can be acute and come on suddenly or as a progressive, long-term condition.
Women and men have varied indications and symptoms of heart disease, particularly when it comes to coronary artery disease. A study shows that gender plays a role in the intensity of early heart disease symptoms. As per the results, both men and women have comparable symptoms of chest pain, but women’s bodies tend to mask the chest pain. It can lead to delayed diagnosis.
A few of the most common symptoms faced by people suffering from heart diseases are:
Unhealthy food, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive smoking, and problematic alcohol consumption are a few of the most prominent risk factors for heart diseases. In addition, increased blood pressure, elevated blood glucose, high blood lipids, and obesity are all risk factors that lead to heart diseases. Most lifestyle diseases imply a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related consequences.
Several factors have a part in deciding if you are at risk for heart disease. For example, women around 55 and men at 45 are more prone to contracting heart diseases. Therefore, it indicates that age plays a role in causing heart disease. People aged 65 and older are much more likely than younger people to suffer or develop heart disease.
Plaque formation is another risk factor. Its formation inside the walls of the coronary arteries restricts blood supply to the heart muscle in cases of coronary artery disease. Ischemia is another term for this. It can be chronic, with the coronary artery contracting with time and restricting blood flow to a significant muscle section. However, it can also be quick, culminating in a plaque rupture and the creation of a thrombus or blood clot.
Another concerning risk factor is high blood pressure. Blood pressure is measured as the pressure inside the blood arteries while blood moves through them in proportion to the heart’s action of pumping or resting. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can gradually lead to the expansion of the heart muscle and stop it from working correctly.
High blood glucose from diabetes damages your cardiac blood vessels and the nerves. Over time, it can lead to heart disease. Moreover, people with diabetes tend to develop heart disease at a younger age than those without it.
Since the prevalence of diabetes has been steadily increasing globally, it directly causes a rise in heart disease cases.
Stress is not uncommon in today’s world. For example, the obsession with competition and perfection leads to undue stress.
And a study shows that psychological stress is a prevalent global factor triggering the onset of heart disease. The damaging effects of stress on the heart cause poor blood circulation and increased chances of stroke.
Modern lifestyle is now equal to junk food, smoking, alcohol, and long hours of gadget use. Over the decades, the modern lifestyle has also made our lives easier. However, people started to compromise their physical fitness.
Diet is one of the crucial factors in lifestyle and directly relates to heart health. Skipping nutritious foods and resorting to fast foods, frozen foods loaded with preservatives can cause heart disease. Along with poor eating habits, lack of exercise and sleep makes the global population vulnerable to heart disease.
Low and middle-income nations account for a minimum of three-quarters of all heart disease fatalities worldwide. In addition, people in low and middle-income countries frequently lack access to basic healthcare facilities that allow for early diagnosis and healthcare. Consequently, disease identification occurs very late after disease progression in many nations. As a result, people die due to heart diseases at a young age, especially youth.
A study shows that the economic level of a country can influence the rate of heart disease progression in their population. Most heart disease cases and deaths are also related to household air pollution and poor diet, which vary by a country’s economic level. In middle income and low-income countries, poor literacy rates, poor diet, and pollution had more substantial effects on heart disease than in high-income countries.
A low-fat, high-fibre diet with lots of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is suitable for preventing heart diseases. In addition, you should consume no more than 2,300 mg of salt every day since excess salt can raise your blood pressure. High blood pressure can trigger heart disease.
You should avoid foods high in saturated fats since they raise the amount of harmful cholesterol in the bloodstream.
Foods containing harmful saturated fats are:
On the other hand, unsaturated fats boost good cholesterol levels and aid in the reduction of artery blockage. Unsaturated foods include:
The most suitable method to have a healthy weight is to combine a balanced diet with frequent exercise. Regular exercise improves the efficiency of the heart and blood circulation system, decreases cholesterol, and maintains a healthy blood pressure level. As per studies, obesity and overweight increase the risk of heart diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain a healthy weight by following a regular exercise schedule.
Regular exercise lowers the chances of getting a heart attack. The heart is also a muscle that improves with exercise, just like any other muscle. A healthy heart can better pump blood around the body. Walking, running, swimming, and dancing are all aerobic exercises that help maintain heart health.
According to studies, quitting smoking will lower the risk of heart disease. Smoking is one of the common causes of atherosclerosis (blockage of the arteries). For people below 50, it remains the most common cause of heart disease. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and blood clots with time. In addition, avoiding tobacco decreases the chance of cardiac arrests, heart attacks, and fatality from other associated heart diseases.
There is an increased chance of high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes if you don’t sleep properly. In addition, these three factors can increase your chances of developing heart disease. Therefore, it is essential to maintain healthy sleep habits.
An average adult needs 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night. If you’re having trouble sleeping, make an appointment with your doctor. People with sleep apnea, for example, stop breathing for short periods during the night. As a result, sleep apnea makes it challenging to obtain a decent night’s sleep and increases your risk of heart disease. If you suffer from sleep apnea, seek treatment as soon as possible.
Cholesterol helps form healthy cells in the body, yet excessive cholesterol levels raise the chance of heart disease. That is because high cholesterol levels cause fat accumulation in the blood vessels. In addition, high cholesterol levels block the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. If a person’s overall cholesterol level is more than 240 mg/dL, LDL level is higher than 160 mg/dL, and HDL level is less than 40 mg/dL, they are more prone to heart disease. You can reduce cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications and (if necessary) medication.
Triglycerides refer to a form of fat found in the bloodstream. High triglyceride levels can also increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease, particularly in women. Therefore, you need to manage it as well. Avoiding simple carbs is one of the best ways to manage triglycerides.
High blood pressure does show any symptoms. However, it is a common cause of heart disease. Therefore, you must take precautionary measures by checking your blood pressure regularly. If you are suffering from heart disease, your doctor may give you medication to alleviate your symptoms and prevent additional complications. If you’ve been prescribed medication, you must take it and follow the instructions properly. Quitting your medicines without visiting a doctor will worsen your symptoms.
Heart disease used to be an issue for the elderly. However, now it is rising as a global health concern, irrespective of age and gender. Identifying individuals at risk for heart diseases and providing them with proper medical treatment can help to reduce premature deaths. Therapy and counselling should be made easily accessible in all primary clinics.
The prevalence of heart disease in young adults has slowly increased due to unhealthy diets, smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity. Fortunately, with a few dietary changes, self-care, and a healthy lifestyle, you can avoid the risk of heart disease.
A: Heart disease comprises a wide range of disorders affecting the heart. The most frequent kinds of heart disease are coronary artery disease, arrhythmia, heart valve disease, and heart failure.
A: Numerous signs hint toward an unhealthy heart. Some of the symptoms are chest ache, shortness of breath, tightness of the chest, and chest discomfort (angina). You might also feel numb, weak and cold legs or arms due to constricted blood vessels and swollen legs (oedema). Pain can also persist around your neck, jaw, throat, upper abdominal, or lower back.
A: There are multiple symptoms related to heart disease. They include nausea, indigestion, heartburn, stomach ache, numbness or weakness of arms and legs, throat or jaw pain, fatigue, excessive snoring or sweating, and irregular heartbeat. If you experience these symptoms regularly, immediately contact your doctor.
A: Coronary artery disease is a severe disorder wherein the heart muscles do not receive sufficient blood and oxygen due to a blockage inside the coronary arteries. The most dangerous outcome of coronary artery disease is the risk of sudden death with no warning. CAD is most common in those who have experienced heart attacks or other forms of cardiac injury.
A: There are many ways to have a healthy heart. Consume nutritious foods, exercise daily, maintain healthy body weight, quit smoking and avoid inhaling passive smoke, maintain a healthy cholesterol and blood pressure level, consume alcohol in moderation, and ease your anxiety. Doing regular checkups is also a good option.
A: Complete cure of heart diseases is not possible. However, through cardiac rehabilitation, the symptoms can be reduced and reversed. Although there is no cure, medical intervention can control symptoms and minimise the risk of strokes and heart attacks. In addition, therapies like adjustments in your lifestyle, such as frequent exercise and quitting smoking, help immensely.
A: Various factors can cause heart damage, including specific disorders, infections, high alcohol consumption, and the toxic effects of medicines like cocaine or chemotherapy treatments. Genetic factors also contribute to it. Another reason can be the inflammation of cardiac muscle (myocarditis).
A: It is possible to reverse heart diseases. Cardiac rehabilitation is among the most effective strategies to do it. Cardiac rehabilitation programmes assist persons with heart disease in regaining their cardiovascular health. Diet, fitness, counselling, and awareness emphasise rehabilitating and preventing future cardiac issues.
A: Multiple symptoms indicate the need for consultation with a medical professional. You need to worry when the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute or when you experience chest discomfort and shortness of breath. An irregular heartbeat can imply thyroid issues, heart problems, atrial fibrillation, or other related diseases.
A: Regular heart checkups and diagnosis should start at 20 years, with periodic tests conducted every 2 to 4 years. Such tests can frequently alert the patient and the physician to any possible cardiac abnormalities before they become significant medical problems. However, once there is a prolonged symptom of heart disease, one should not delay and get checked immediately.
A: Generally, dark chocolate has a lot of flavonoids, especially flavonols, which decrease the risk of heart disease. In addition, the consumption of cocoa or chocolate reduces the risk of insulin resistance and high blood pressure. A healthy level of insulin and blood pressure indicates a healthy heart. 75-100% dark chocolates or pure cacao powder is a better choice for more benefits.

